Unit 2: Biological Basis of Behavior
|
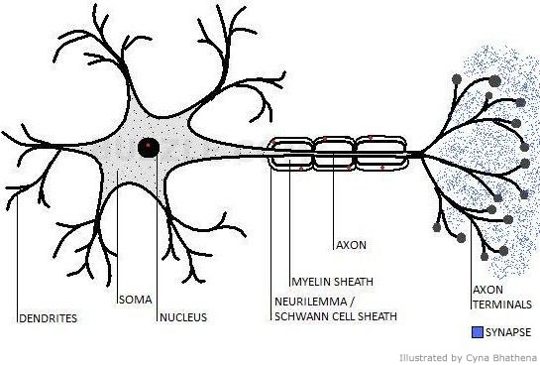
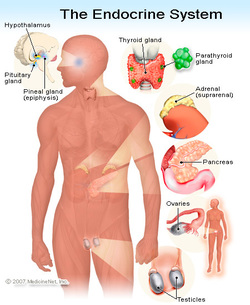
The physical structures that form our nervous systemThe physical structures that form our endocrine system |
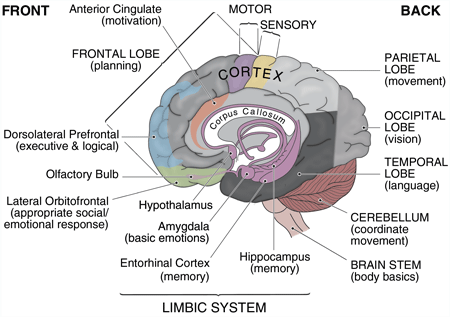
How genetics can affect human behaviorThe unique functions and abilities of the brainBrain Resources:
The Behaving Brain -DISCOVERING PSYCHOLOGY The Responsive Brain - DISCOVERING PSYCHOLOGY Explore the Brain and Mind: BrainFacts.org The Brain Teaching Modules The Unfixed Brain The Mind Teaching Modules Meet Your Master: Getting to Know Your Brain - Crash Course Psychology #4 Sleep and Dream Resources: Consciousness - Crash Course Psychology #8 To Sleep, Perchance to Dream - Crash Course Psychology #9 Altered States - Crash Course Psychology #10 |
|
|