Unit 9: Social Psychology
Social Psychology
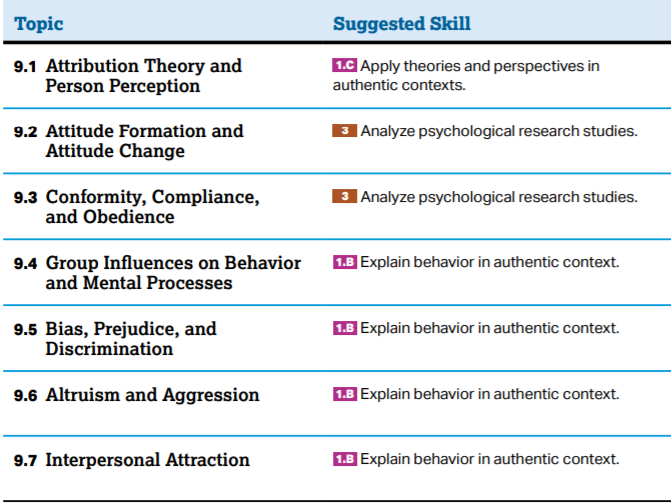
How do we explain (or "attribute") the behavior of others? What impact do these "attributions" have on individuals and on society as a whole? How are individuals affected by a group? Under what conditions do people obey, conform, make friendships, find love and help others? How do attitudes and actions influence individual and group behavior?How do psychologists define culture? What influence does culture have on individuals and groups? Psychologists focus on a variety of social phenomena when exploring how we relate to one another in social situations. We will learn what their research reveals about the structure and function of groups; the basic concepts of social cognition and attribution; the key studies that have contributed to the body of knowledge about social relations; and, the social psychologist's perspective of organizational behavior (e.g., businesses, etc.).
Unit Objectives
Social Thinking
1. Describe the three main focuses of social psychology, and explain how the fundamental attribution error impacts our judgments of others.
2. Define attitude, and explain how attitudes and actions affect each other.
Social Influence
3. Describe the chameleon effect, and discuss Asch’s experiments on conformity, noting the difference between normative and informational social influence.
4. Describe Milgram’s experiments on obedience, and explain how the conformity and obedience studies can help us understand our susceptibility to social influence.
5. Describe the conditions in which the presence of others is likely to result in social facilitation, social loafing, or deindividuation.
6. Discuss how group interaction can facilitate group polarization and groupthink.
7. Describe how behavior is influenced by cultural norms.
8. Identify the characteristic common to minority positions that successfully sway majorities.
Social Relations
9. Identify the three components of prejudice, and contrast overt and subtle forms of prejudice.
10. Discuss the social factors that contribute to prejudice, and explain how scapegoating illustrates the emotional component of prejudice.
11. Cite three ways that cognitive processes help create and maintain prejudice.
12. Explain how psychology’s definition of aggression differs from everyday usage, and describe various biological influences on aggression.
13. Outline psychological and social-cultural triggers of aggression, noting the relationship between violent video games and aggressive behavior.
14. Describe the influence of proximity, physical attractiveness, and similarity on interpersonal attraction.
15. Describe the effect of physical arousal on passionate love, and identify two predictors of enduring companionate love.
16. Define altruism, and describe the steps in the decision-making process involved in bystander intervention.
17. Explain altruism from the perspective of social exchange theory and social norms.
18. Explain how social traps and mirror-image perceptions fuel social conflict, and discuss effective ways of encouraging peaceful cooperation and reducing social conflict.
Resources
The Power of the Situation -DISCOVERING PSYCHOLOGY
Constructing Social Reality-DISCOVERING PSYCHOLOGY
Khan Academy Videos
Philip Zimbardo: The Psychology of Evil
Taking a Closer look at Milgram's Obedience Studies
Social Thinking: Crash Course Psychology #37
Social Influence: Crash Course Psychology #38
Prejudice & Discrimination: Crash Course Psychology #39
Aggression V. Altruism: Crash Course Psychology #40
10 Famous Psychological Experiments That Could Never Happen Today
Unit Objectives
Social Thinking
1. Describe the three main focuses of social psychology, and explain how the fundamental attribution error impacts our judgments of others.
2. Define attitude, and explain how attitudes and actions affect each other.
Social Influence
3. Describe the chameleon effect, and discuss Asch’s experiments on conformity, noting the difference between normative and informational social influence.
4. Describe Milgram’s experiments on obedience, and explain how the conformity and obedience studies can help us understand our susceptibility to social influence.
5. Describe the conditions in which the presence of others is likely to result in social facilitation, social loafing, or deindividuation.
6. Discuss how group interaction can facilitate group polarization and groupthink.
7. Describe how behavior is influenced by cultural norms.
8. Identify the characteristic common to minority positions that successfully sway majorities.
Social Relations
9. Identify the three components of prejudice, and contrast overt and subtle forms of prejudice.
10. Discuss the social factors that contribute to prejudice, and explain how scapegoating illustrates the emotional component of prejudice.
11. Cite three ways that cognitive processes help create and maintain prejudice.
12. Explain how psychology’s definition of aggression differs from everyday usage, and describe various biological influences on aggression.
13. Outline psychological and social-cultural triggers of aggression, noting the relationship between violent video games and aggressive behavior.
14. Describe the influence of proximity, physical attractiveness, and similarity on interpersonal attraction.
15. Describe the effect of physical arousal on passionate love, and identify two predictors of enduring companionate love.
16. Define altruism, and describe the steps in the decision-making process involved in bystander intervention.
17. Explain altruism from the perspective of social exchange theory and social norms.
18. Explain how social traps and mirror-image perceptions fuel social conflict, and discuss effective ways of encouraging peaceful cooperation and reducing social conflict.
Resources
The Power of the Situation -DISCOVERING PSYCHOLOGY
Constructing Social Reality-DISCOVERING PSYCHOLOGY
Khan Academy Videos
Philip Zimbardo: The Psychology of Evil
Taking a Closer look at Milgram's Obedience Studies
Social Thinking: Crash Course Psychology #37
Social Influence: Crash Course Psychology #38
Prejudice & Discrimination: Crash Course Psychology #39
Aggression V. Altruism: Crash Course Psychology #40
10 Famous Psychological Experiments That Could Never Happen Today