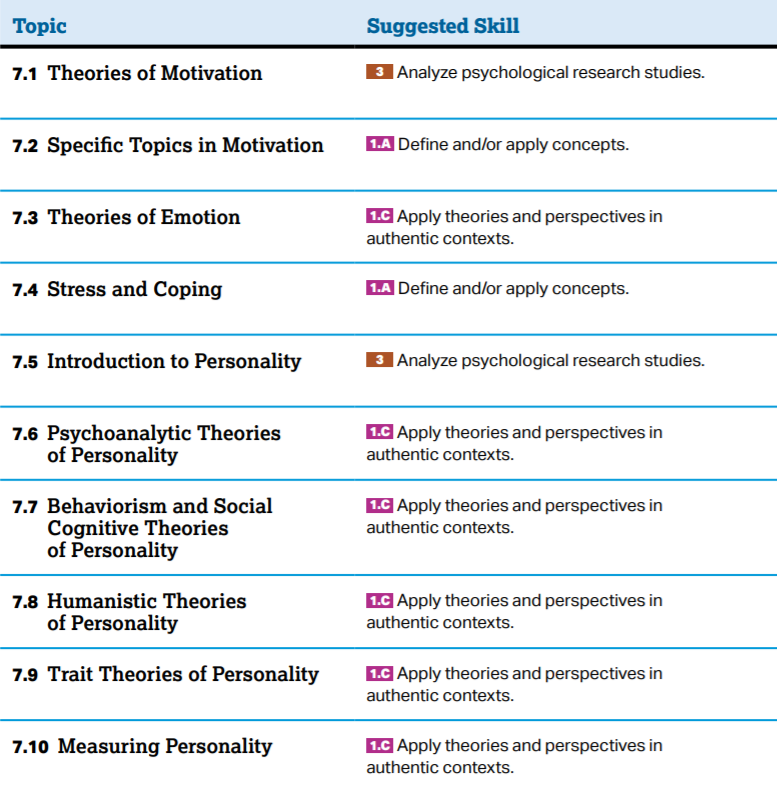
Motivation
|
Unit Objectives
|
Emotion |
Unit Objectives
Resources Motivation and Emotion- DISCOVERING PSYCHOLOGY Emotion, Stress and Health: Crash Course Psychology #26 Let's Talk About Sex: Crash Course Psychology #27 |

Personality
How do psychologists define and study personality? What advantages and limitations exist for each of the psychologists' theoretical description of personality? How do psychologists reliably measure personality and interpret personality's role in behavior? Psychologists agree that "Personality is one’s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting." What differs is the many ideas about how our personality develops.We will explore the major theories and approaches to personality (psychoanalytic/psychodynamic, humanistic, cognitive,trait, social learning and behavioral). We will also learn about research, the differences among research orientations, and the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
Unit Objectives
I. Introduction and the Psychoanalytic Perspective
Define personality, and explain how Freud’s treatment of psychological disorders led to his study of the unconscious mind.
Describe Freud’s view of personality structure in terms of the id, ego, and superego.
Identify Freud’s psychosexual stages of development, and describe the effects of fixation on behavior
Discuss how defense mechanisms serve to protect the individual from anxiety.
Contrast the views of the neo-Freudians and psychodynamic theorists with Freud’s original theory.
Describe two projective tests used to assess personality, and discuss some criticisms of them.
Summarize psychology’s current assessment of Freud’s theory of psychoanalysis, including its portrayal of the unconscious.
II. The Humanistic Perspective
Describe the humanistic perspective in terms of Maslow’s focus on self-actualization and Rogers’ emphasis on people’s potential for growth.
Explain how humanistic psychologists assessed personality, and discuss the major criticisms of the humanistic perspective on personality.
III. The Trait Perspective
Discuss psychologists’ interests in personality types, and describe research efforts to identify fundamental personality traits.
Discuss the value of using personality inventories to assess traits, and identify the Big Five trait dimensions.
Summarize the person-situation controversy, and explain its importance as a commentary on the trait perspective.
IV. The Social-Cognitive Perspective
Describe the social-cognitive perspective, and discuss the important consequences of personal control and optimism.
Explain why social-cognitive researchers assess behavior in realistic situations, and state the major criticism of the social-cognitive perspective.
V. Exploring the Self
Explain why psychology has generated so much research on the self, and discuss the importance of self-esteem to human well-being.
Discuss some evidence for self-serving bias, and contrast defensive and secure self-esteem.
Identify some ways a primarily individualist culture differs from a primarily collectivist culture.
Resources
Khan Academy Videos on Biological, psychological, and socio-cultural factors influence behavior and behavior change.
Rorschach & Freudians: Crash Course Psychology #21
Measuring Personality: Crash Course Psychology #22
Personality Test
How do psychologists define and study personality? What advantages and limitations exist for each of the psychologists' theoretical description of personality? How do psychologists reliably measure personality and interpret personality's role in behavior? Psychologists agree that "Personality is one’s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting." What differs is the many ideas about how our personality develops.We will explore the major theories and approaches to personality (psychoanalytic/psychodynamic, humanistic, cognitive,trait, social learning and behavioral). We will also learn about research, the differences among research orientations, and the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
Unit Objectives
I. Introduction and the Psychoanalytic Perspective
Define personality, and explain how Freud’s treatment of psychological disorders led to his study of the unconscious mind.
Describe Freud’s view of personality structure in terms of the id, ego, and superego.
Identify Freud’s psychosexual stages of development, and describe the effects of fixation on behavior
Discuss how defense mechanisms serve to protect the individual from anxiety.
Contrast the views of the neo-Freudians and psychodynamic theorists with Freud’s original theory.
Describe two projective tests used to assess personality, and discuss some criticisms of them.
Summarize psychology’s current assessment of Freud’s theory of psychoanalysis, including its portrayal of the unconscious.
II. The Humanistic Perspective
Describe the humanistic perspective in terms of Maslow’s focus on self-actualization and Rogers’ emphasis on people’s potential for growth.
Explain how humanistic psychologists assessed personality, and discuss the major criticisms of the humanistic perspective on personality.
III. The Trait Perspective
Discuss psychologists’ interests in personality types, and describe research efforts to identify fundamental personality traits.
Discuss the value of using personality inventories to assess traits, and identify the Big Five trait dimensions.
Summarize the person-situation controversy, and explain its importance as a commentary on the trait perspective.
IV. The Social-Cognitive Perspective
Describe the social-cognitive perspective, and discuss the important consequences of personal control and optimism.
Explain why social-cognitive researchers assess behavior in realistic situations, and state the major criticism of the social-cognitive perspective.
V. Exploring the Self
Explain why psychology has generated so much research on the self, and discuss the importance of self-esteem to human well-being.
Discuss some evidence for self-serving bias, and contrast defensive and secure self-esteem.
Identify some ways a primarily individualist culture differs from a primarily collectivist culture.
Resources
Khan Academy Videos on Biological, psychological, and socio-cultural factors influence behavior and behavior change.
Rorschach & Freudians: Crash Course Psychology #21
Measuring Personality: Crash Course Psychology #22
Personality Test